In a recent study, it was demonstrated that 82% of businesses believe there is a strong correlation between creativity and business outcomes. In this context, design thinking has emerged as a powerful tool to foster creativity and drive growth.
However, despite the increasing popularity of design thinking, there still exist many misconceptions within the business community about it. Below are 5 common misconceptions that we need to identify and overcome.
Table of Contents
Misconception 1: Design Thinking Is Exclusively for the Creation of New Products.
There’s a common belief that after user research, specific details about the product’s form will be revealed. People undertake user research with the hope that its findings will immediately inform designers about what needs to be done to achieve an effective design.
However, while user research provides valuable insights for product design, it doesn’t automatically generate detailed and specific design solutions. Discoveries from user research can contribute to innovation, but they don’t directly create innovation. It may require additional efforts from iterative software development cycles.
This remains one of the biggest misconceptions about design thinking – something forward-thinking IT organizations are quickly debunking. “Design thinking can also be applied to services, processes, strategies, scenario development, and project roadmap sessions. It can be used wherever there’s a need for creative solutions,” says Yugal Joshi, Vice President of Everest Group.
IT leaders who believe they can only apply design thinking to new situations are missing crucial opportunities to rethink existing processes and solutions.
Misconception 2: User Research Adds Additional Costs to the Project
Companies often build their products entirely based on their assumptions about end users, without involving real users in the design process because they are reluctant to incur the time and monetary costs associated with user research. Businesses tend to view user research as an additional expense in terms of both time and money.
However, the real question is: how should that time and money be best utilized to create something beneficial for optimal product design? The truth is, the cost of not understanding users is much greater. Producing something that doesn’t align with user needs and expectations can lead to poorly designed solutions, thus resulting in higher costs and time spent on product fixes.
Misconception 3: Users Tend to Be More Emotional Than Rational
While classical economics has taught us that users make decisions based on a careful analysis of costs and expected utility, research results indicate that people tend to make decisions based on emotions rather than reason. According to neuroscientist Antonio Damasio, “Even with what we believe are logical decisions, the point of choice is always based on emotion.”
Therefore, designers should understand human decision-making and go beyond the ability to create products that effectively influence our behavior.
Misconception 4: In Human-Centered Design, We Only Focus on the User
The human factor is indeed the central focus of human-centered design in APAC. However, it’s not the only factor considered throughout the entire design process.
Human factors, social factors, and technological factors all interact with each other and impact human activities and emotions. Since these factors interact and directly influence users as well as how we shape product or service designs, we should carefully consider all these related factors throughout the process to achieve the goal of implementing human-centered design methodology effectively.
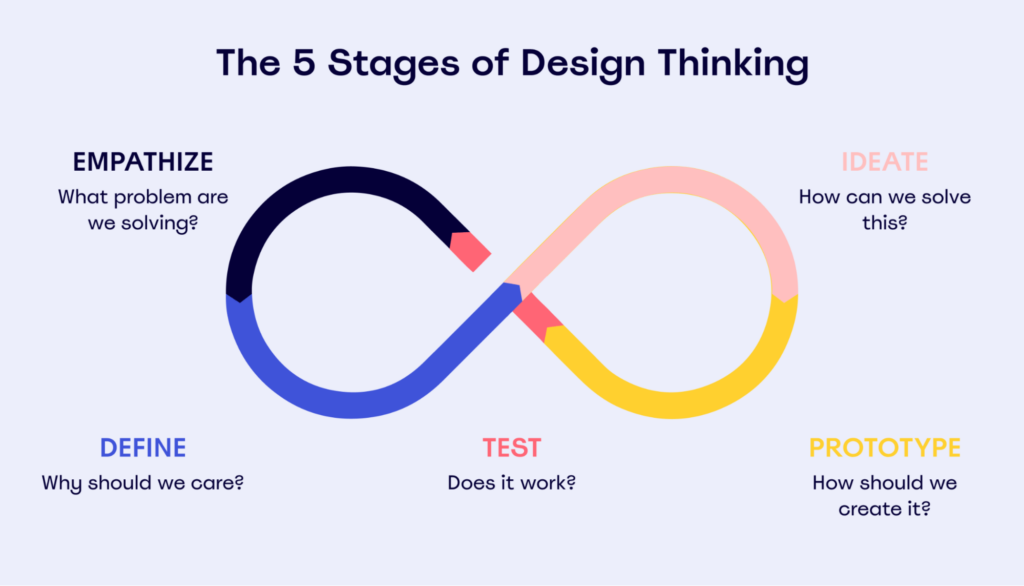
Misconception 5: Design Thinking Is a Linear Process
Design Thinking is a methodology that fosters innovation, but it’s crucial to note that Design Thinking is a non-linear process. For instance:
- You can transition from Experimentation to Ideation: Experimentation can spark new ideas for a project.
- You can transition from Prototype to Idealization: Learn from prototypes to ignite new ideas.
- You can transition from Experimentation to Empathy: Understand users through experimentation.
Why Is a User-Centered Solution Important?
A website, application, or product exists to satisfy consumers, so its success depends on their experience.
The benefits of user-centered design for a business include:
- User loyalty keeps returning to business
- Increased revenue
- Developing sophisticated, efficient, and accessible products
- Understanding issues deeply to create excellent solutions
- Collaboration between customers and teams
- Avoiding common errors
- Enhancing competitive capacity
- Helping them understand their market
In addition, a user-centered design also benefits consumers by:
- Simplifying their lives.
- Fulfilling their desires.
- Making them feel listened to and understood by businesses.
- Making them feel valued in the development of the products they use.
- Providing solutions to problems they may not know they have or cannot imagine solutions for.
User-Centered Design Process
Each stage of the user-centered design process focuses on the needs and desires of the users. It’s an iterative process where designers continually adjust and refine a business’s product to ensure it best serves the target users.
At the heart of the UCD process lies understanding and empathy towards users. It’s not just about what a product provides to users, but also about the interaction experience with the design and how it makes users feel. Below are the pivotal steps in the user-centered design process:
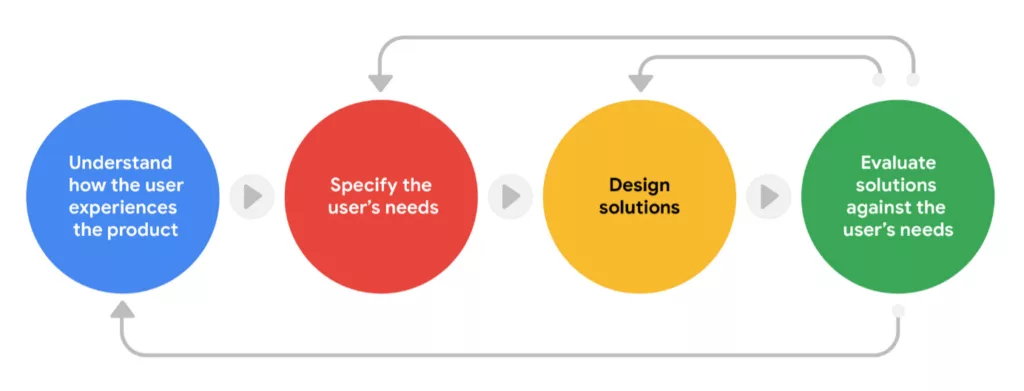
- To understand how users experience your product, it’s crucial to know how they will interact with your design and in what context they will use the product. Achieving this requires extensive research, including observing user behaviors and conducting interviews, which we will delve into further in the following sections.
- Next, you need to clearly identify the users’ needs. Based on your research, pinpoint which of the users’ issues are most critical to address.
- Then, you need to propose design solutions. Present multiple ideas for designs that can address the users’ identified issues. Then, start actually designing those ideas!
- Once you have the designs, you need to evaluate them against the users’ needs. Ask yourself: Does my design solve the users’ problem? To answer this question, you should test the product with real users and gather feedback.
Additionally, you can apply various software development processes such as the waterfall model, agile, or other models, depending on the specific needs of the project.
Prominent design thinking tools and techniques in 2024
Below are the most prominent design thinking tools and techniques to know in 2024:
- Miro – The most versatile design thinking tool.
- FigJam by Figma – Best for highly flexible virtual whiteboarding.
- UserTesting – Ideal for obtaining video feedback from users.
- Invision – The best tool for creating richly interactive prototypes.
- Marvel – Best for rapid prototyping and testing.
- Stormboard – The most effective tool for building collaborative workspaces.
Transforming Digital Experiences: The Power of UX Design in Singapore
Singapore has emerged as a hub for innovation and technology, and user experience design in Singapore plays a crucial role in shaping the success of businesses in the region. With a focus on creating seamless and intuitive digital experiences for users, UX designers in Singapore leverage cutting-edge methodologies and technologies to craft products that delight and engage users.
At Vinova, we understand the critical role that user experience plays in the success of digital products and services. As a top-tier technology firm in Singapore, we specialize in delivering exceptional user experiences through our innovative UX design solutions.
In conclusion, dispelling these five common myths about design thinking highlights the core of genuine user-centered solutions. Understanding that design thinking goes beyond product creation, that user research is an essential investment, and that user behavior is shaped by both emotion and reason, enables us to create more impactful designs. Ready to elevate your business with innovative, user-focused solutions? Contact Vinova today and let’s make it happen.